SCHEDULING STEPS FOR PROJECT MANAGEMENT HANDLING
Preliminary information requirements:
Identification of project difficulties
Vision, mission, services and processes
- Current difficulties
- Provisions for risks.
- Established management system
- Applicable legal requirements, standards, procedures, protocol requirements and file structure
- Taxonomy.
7.OBS
- Contracts
- Charter Plans – WBS

PMH SCHEDULING CONSIDERATIONS 2
Scheduling means uncertainties.

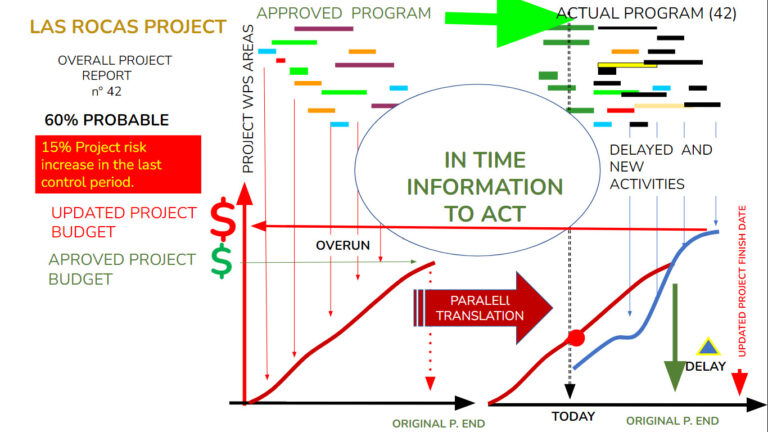
Uncertainties of the project in availabilities, productivities, competences and capacities of the collaborators, prices of inputs, etc., hence the need to determine the acceptable project risk (%) to the owner in terms of terms and costs.
The schedule is the map and the compass of the project to know the route to follow, the progress, people, resources, money, and necessary time.

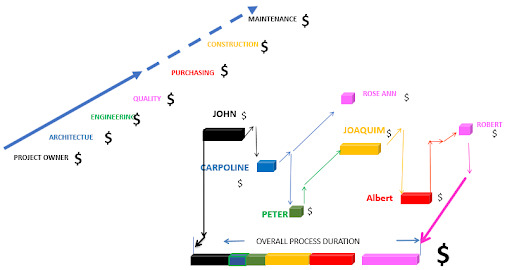
n the relay races that constitute the project, visualize the sticks –kuantos- of each race to identify the runners who carry them and know where they go.
PMH SCHEDULING CONSIDERATIONS 3

Scheduling to produce a schedule for knowing what to do, when, in how long, who should do it, and how many labor hours should be spent.

Cash flow and resources needed over time

Reporting to stakeholders
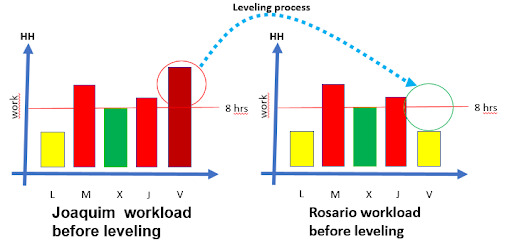
PROJECT WORK LEVELING FOR REALISTIC SCHEDULE
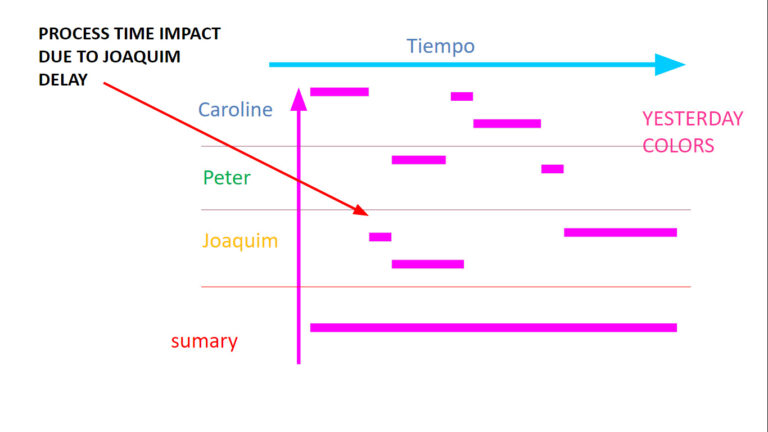
What is for the coming week Joaquim’s workload?
Would overtime be approved? Who could take part of the load?
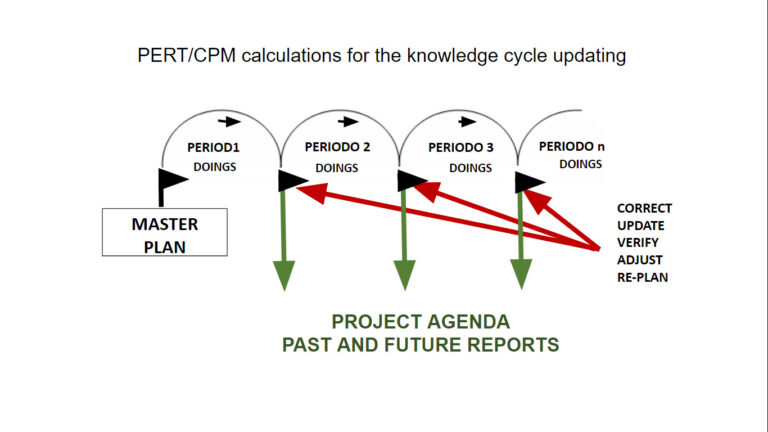
Most common Project Management Reports
- Workloads and idle capacity.
- Business, projects and people performance.
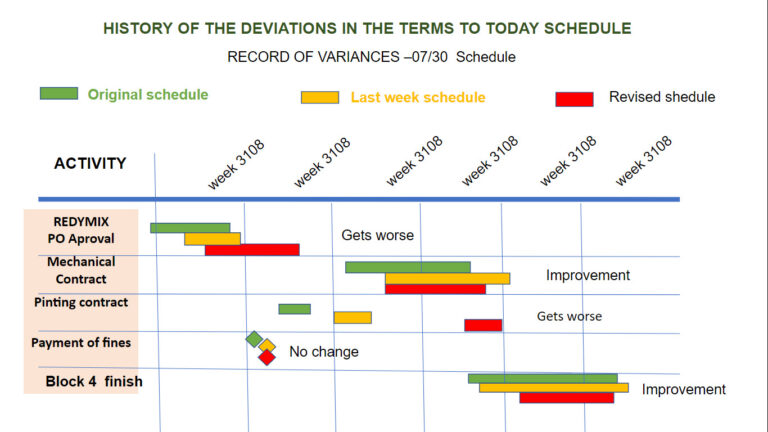
- Project difficulties and deviations analysis.
- Contingencies updating.
- Project progress (%), time, expenses and forecasts to finish.
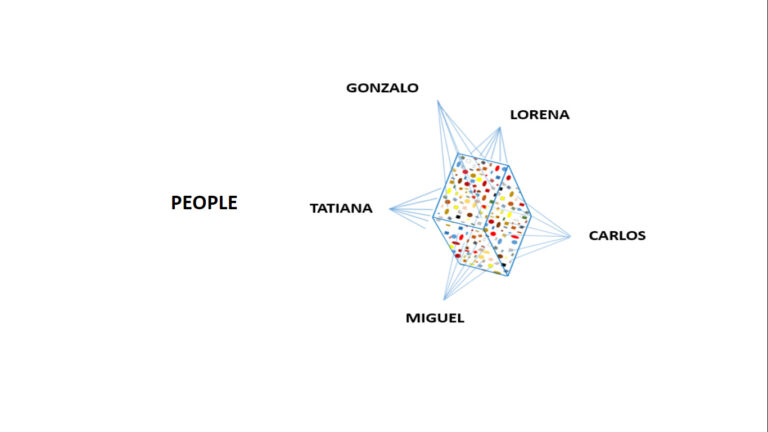
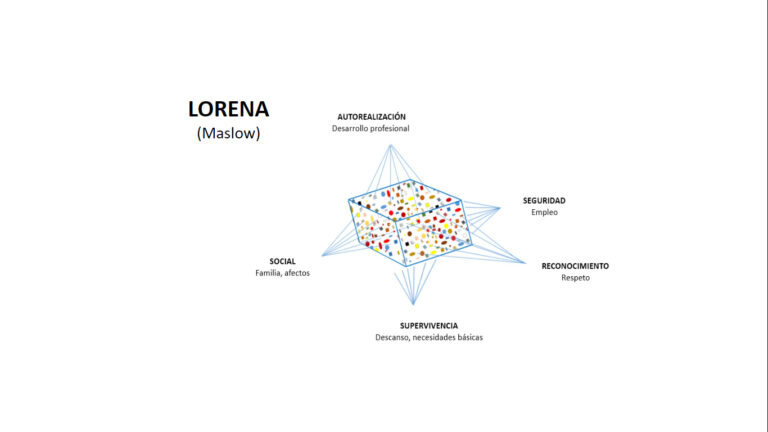
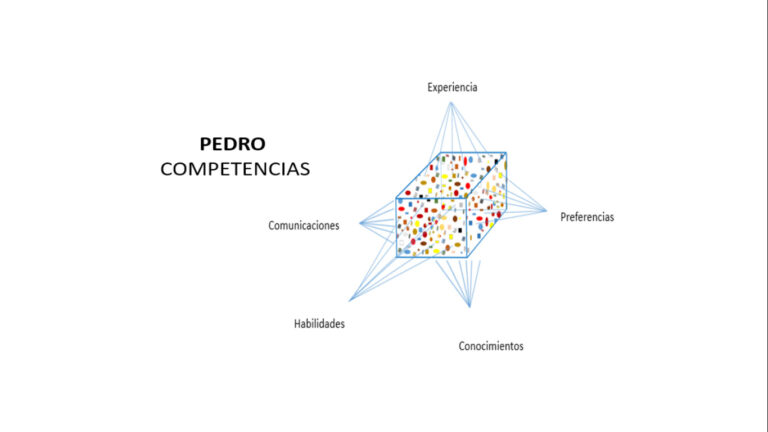
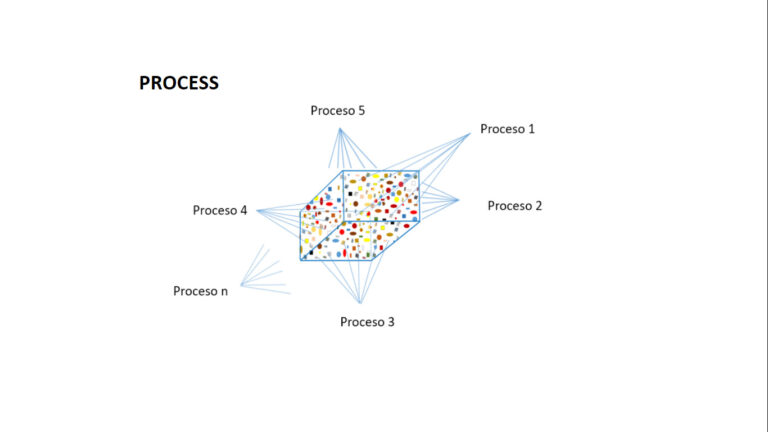
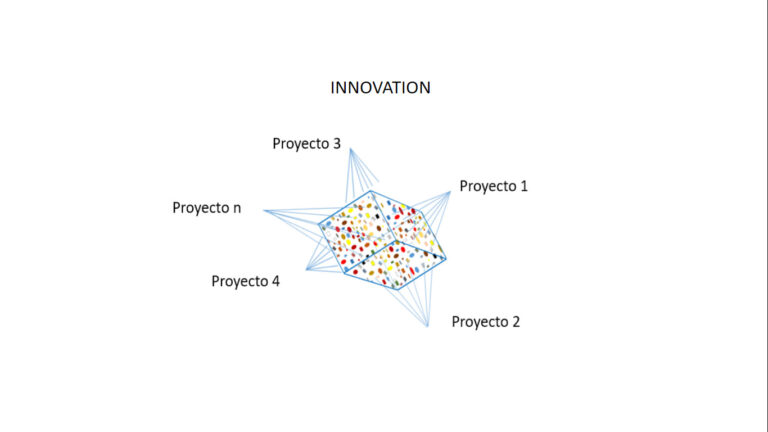
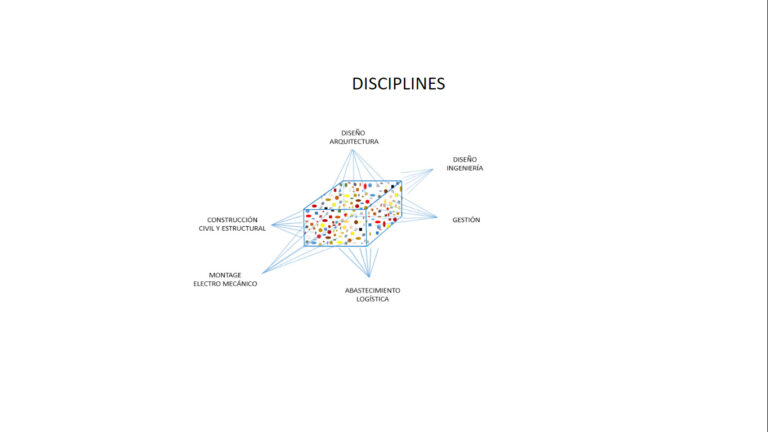
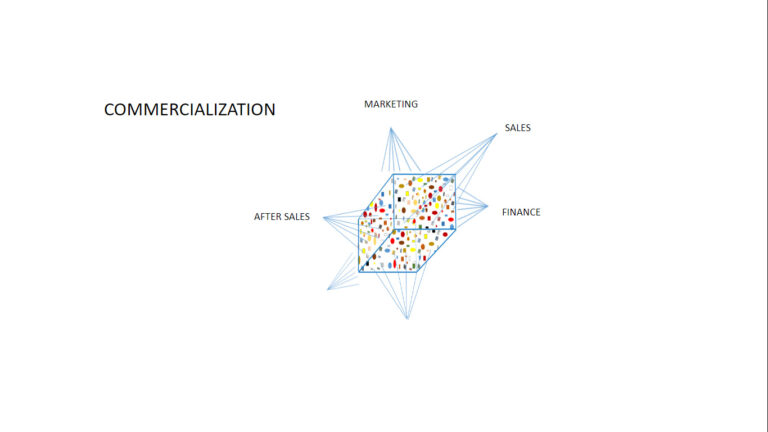
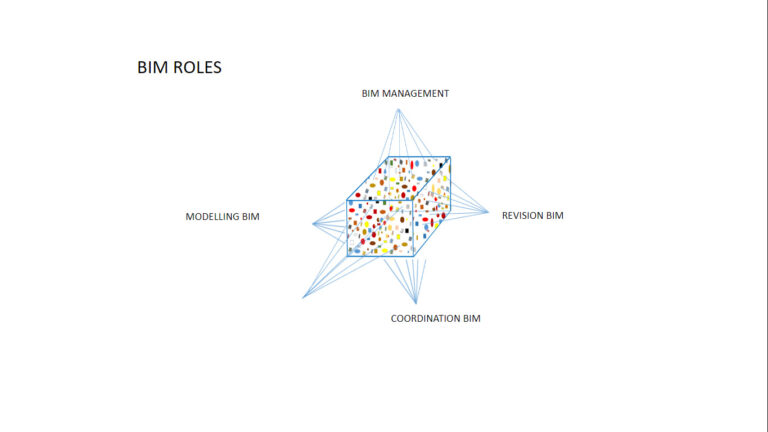
For project analysis and difficulties identification, the following slides show a few examples of project kuantos selected with different criteria for different purposes.
Detailed information organized according to disciplines.